Information classification
Hot news
What are the synthesis methods of alkyl glycosides?
2024-09-11 14:37
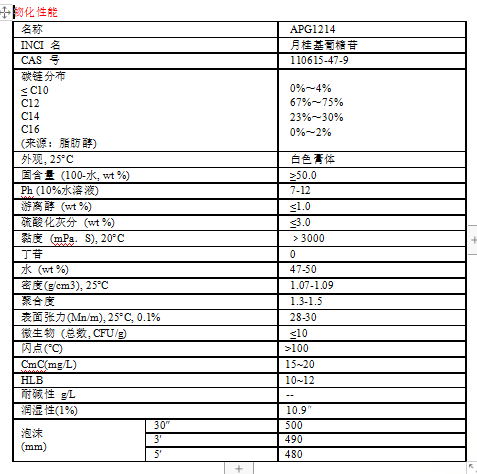
What are the performance characteristics of alkyl glycosides?
2024-09-11 14:36
What is the one-time usage amount of alkyl glucoside?
2024-09-11 14:35
What does the HLB value of alkyl glycosides mean?
2024-09-11 14:34
The main use of alkyl glycosides!
2024-09-11 14:32
What is alkyl glycoside surfactant?
2024-09-10 14:16
What are the amidation reagents?
Source:
2024-08-23 14:29
Author:
Source:
Amide reagents play an important role in organic synthesis, especially in the formation of amide bonds. Here are some common amidation reagents and their characteristics:

1.Carbodiimide based condensing agents
- DCC (Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide): It is inexpensive, but the DCU generated in the reaction has low solubility in DMF, resulting in a white precipitate. Therefore, it is generally not used in solid-phase synthesis, but can be removed by filtration in liquid-phase synthesis and has a wide range of applications. DCC HOBt composite condensing agent is currently the most widely used condensation method.
- DIC, EDC, BDDC: These reagents are also widely used in the large-scale preparation of peptides and are relatively inexpensive. EDC.HCl is water-soluble and is commonly used in the connection between peptides and proteins, with good results. But it is generally not used alone, and reagents such as HOBt and HOAt need to be added during the activation process to control their side reactions.
2. Onium salt condensing agent
- HATU (O - (7-Azabenzotriazol-1-yl) - N, N, N ', N' - tetramethylurea hexafluorophosphate): has a good condensation effect, but is relatively expensive. Commonly used in amidation reactions that require high activity and high yield.
- HBTU, PyBOP (benzotriazole-1-yloxytriphyrrolidine phosphate), BOP: These reagents also have high activity and are used for amidation reactions that are difficult to carry out by other methods.
3. Active ester method reagents
- CDI (carbonyl diimidazole): As a carboxylic acid activating reagent, highly active and relatively stable acyl imidazoles can be obtained, which can then react with amines to obtain amides. This method is commonly used for amide synthesis in the active ester method.
4. Acyl chloride method reagent
- Acyl chloride: The reaction of acyl chloride with ammonia or amine is a convenient method for synthesizing amides. The preparation of acyl chlorides is commonly achieved by reacting reagents such as SOCl2, POCl3, PCl5 with carboxylic acids. The reaction between acyl chloride and amine needs to be carried out in an ice water bath, and may require the addition of DMAP or DMF catalysis, as well as the addition of bases such as triethylamine, pyridine, etc. to remove the hydrogen halides produced by the reaction.
5. Other reagents
- TEA (triethylamine) and DIEA (diisopropylethylamine): These are commonly used bases for acid amine condensation. The possibility of racemization caused by DIEA is low for chiral reactions.
- Inorganic bases, such as K2CO3, can be used for the condensation of phenylamine to avoid the formation of esters.

Choose Suggestions
- When selecting amidation reagents, priority should be given to reagents with mild reaction conditions, high yields, and fewer side reactions.
- For substrates with steric hindrance, high activity condensing agents such as HATU and PyBOP can be considered.
- If large-scale preparation is required, inexpensive reagents such as DCC and EDC are good choices.
- In specific applications, suitable amidation reagents need to be selected based on the properties of the substrate, reaction conditions, and the requirements of the target product.
Please note that the above information is for reference only, and the specific selection should be based on experimental conditions and requirements.





